Patients Could Have Sexual Intercourse and Had Improved Quality of Life After Botox.1
Invasive Treatments for Vaginismus or Dyspareunia
The invasive treatments for Vaginismus and Dyspareunia are quite limited as surgery is not usually an effective treatment option for these conditions. If you are suffering from Dyspareunia, your doctors will work to investigate the root cause. In some cases, surgery to treat the cause may be offered, for example if you have pelvic organ prolapse or endometriosis that requires surgery. On this page, we will review the invasive treatments that are available.
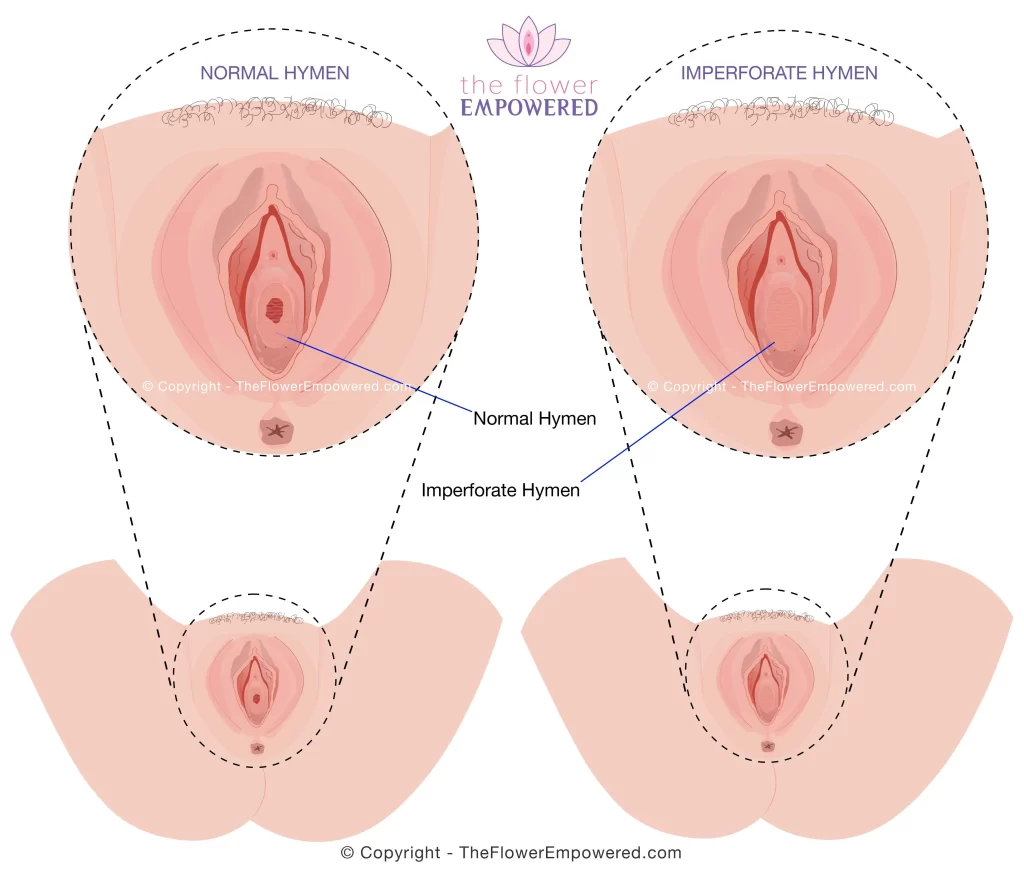
Hymenectomy for an Imperforate Hymen
They hymen is a small band of tissue that surrounds the vaginal opening. This tissue is generally broken during penetration. Sometimes the hymen tissues can be rigid making it difficult or impossible to penetrate. This is known as an imperforate hymen which is uncommon happening only in 0.05–0.1% of women2. In cases where an imperforate hymen is the cause of vaginismus, a hymenectomy may be offered as a surgical treatment.
The surgeon will carefully perforate the hymen taking care to avoid the muscle tissues. This is a very precise surgery, the purpose of which is to solely remove the excess tissues of the hymen. In the 1990s, the hymenectomy was often combined with an episiotomy (cutting the perineum) which was found to be an ineffective treatment, with one 2001 study finding that it fails to address the mechanism of vaginismus, leaving the patient with an unresolved problem yet with the added trauma of the surgery coupled with visible physical alterations.3
The NHS website in the UK states that “Sometimes vaginismus is mistaken for a physical problem with your vagina, which can lead to needless surgery. Very few cases of vaginismus require surgery.” Therefore, If you are offered a surgery to treat your vaginismus without the presence of an imperforate hymen, you should seek a second opinion, particularly if the surgery itself will involve cutting your pelvic floor muscles.
Botox for Vaginismus
Botox is a more invasive treatment where botulinum toxin is injected into pelvic floor muscles to prevent muscular contraction. Although no incisions are made, this treatment is typically given under anaesthetic (either local or general depending on the severity of the vaginismus). The treatment is a two step process.
Step 1 – Botox Administration
Once you have been given either a local or a general anaesthetic, your surgeon will attempt to identify the muscles which are most impacted. Botox will be injected into the pelvic floor muscles in order to relax the muscles.
Step 2 – In Place Dilation
A pain relieving topical cream will be applied and a dilator inserted into the vagina. This dilator will be left in place either for a few hours while in recovery or sometimes overnight. It completely depends on your surgeons preferences.
Following the botox treatment, you will be instructed how to do dilation, which should be performed daily following the treatment. Botox can also be used as a treatment for dyspareunia but the dilation isn’t required in those cases.
Some research4 suggests that when comparing Botox directly with physiotherapy alone, botox was not as effective in treating sexual functioning including successful intercourse, desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, satisfaction, and pain. Botox is best when combined with physiotherapy and other conservative therapies.
Treatment Options for Vaginismus and Dyspareunia
Having reviewed the invasive treatments for vaginismus and dyspareunia, you may be interested in reviewing the conservative treatments. You can do that by clicking the button below. If you did not find what you were looking for, you can search this site using the search bar at the bottom of the page.
Explore the Types of Sexual Dysfunction
You may be interested in exploring the types sexual dysfunction. You can do that from here:
References
- Sorensen J, Bautista KE, Lamvu G, Feranec J. Evaluation and Treatment of Female Sexual Pain: A Clinical Review. Cureus. 2018 Mar 27;10(3):e2379. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2379. PMID: 29805948; PMCID: PMC5969816.
- Ditza Katz, Ross Lynn Tabisel, Is surgery the answer to vaginismus?, Obstetrics & Gynecology, Volume 97, Issue 4, Supplement 1, 2001, Page S27, ISSN 0029-7844, https://doi.org/10.1016 S0029-7844(01)01203-0.
- Lee KH, Hong JS, Jung HJ, Jeong HK, Moon SJ, Park WH, Jeong YM, Song SW, Suk Y, Son MJ, Lim JJ, Shin JI. Imperforate Hymen: A Comprehensive Systematic Review. J Clin Med. 2019 Jan 7;8(1):56. doi: 10.3390/jcm8010056. PMID: 30621064; PMCID: PMC6352236.
- Wells C, Farrah K. Injectable Botulinum Toxin for Pelvic Pain: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness, Cost-Effectiveness, and Guidelines [Internet]. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2019 Aug 22. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549463/.